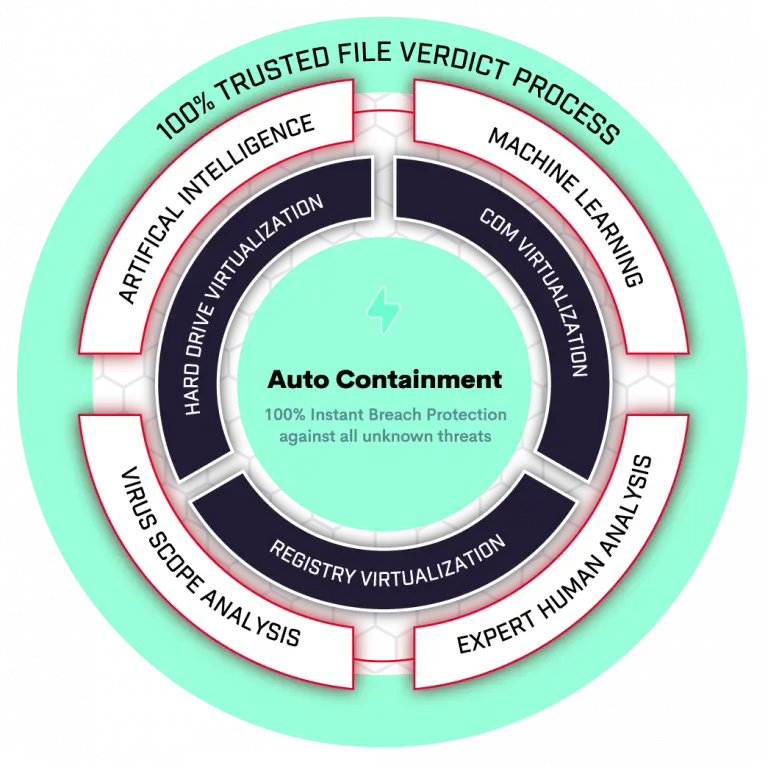
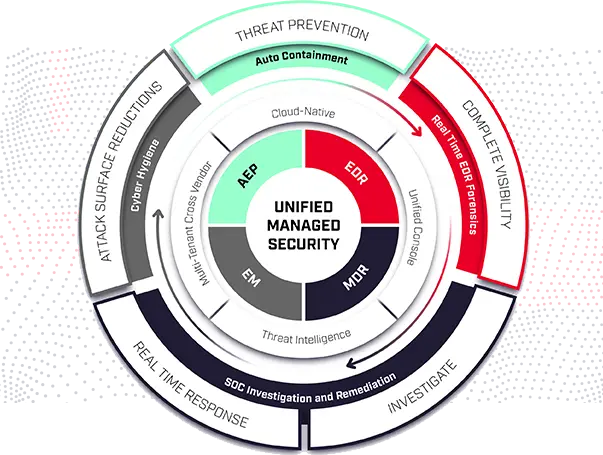
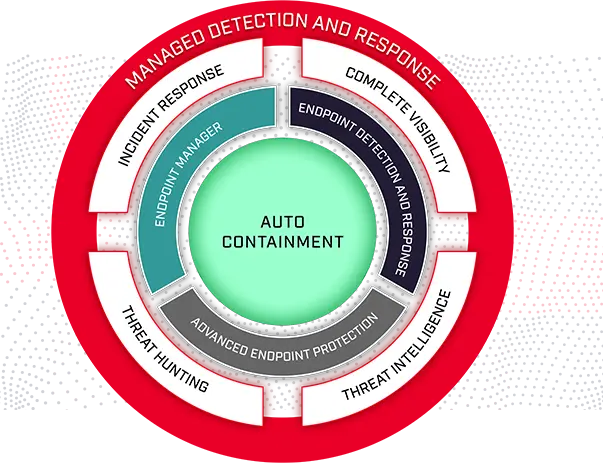
The Endpoint Detection and Response(EDR) Solutions consists of products that monitor and store endpoint-system-level behaviors, employ a variety of data analytics techniques to identify suspicious system behavior, offer contextual data, thwart malicious activity, and offer recommendations for corrective action to restore harmed systems. The following four fundamental capabilities are required for EDR solutions:
- Identify security issues
- Stop them at the endpoint
- Look into security incidents
- Provide remediation advice
EDR systems defend against common attack strategies, methods, and techniques that initial access brokers frequently employ, including fileless malware, malicious scripts, contaminated attachments, stolen user credentials, etc.
An EDR solution keeps track of every activity at the endpoints and provides thorough real-time visibility and threat information. With incident data search, alert triage, suspicious activity detection and containment, and threat hunting, it provides enhanced threat detection, investigation, and response capabilities.
You may need to select an EDR solution that is appropriate for your requirements, which may include your industry, size, security department make-up, tools used, other vendors, and environment. The other questions you should be asking your EDR provider are as follows:
How does it identify threats and anomalies?
- What scope does it offer?
- What level of added organizational complexity is it causing?
- Is it wise and useful to not provide the administrators access, any operational bottlenecks?